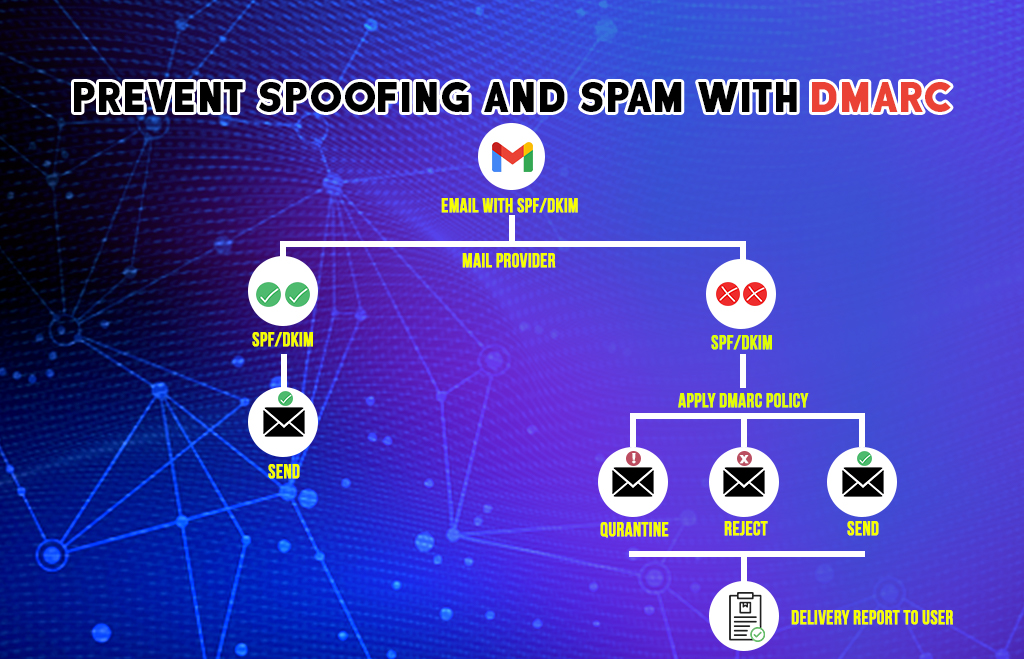
How to Setup / add / update DMARC Record?
Google Workspace uses mail standards like DMARC to prevent mail spoofing and phishing. It helps prevent messages from being marked as spam. Login to your hosting service provider and find the DNS records. Workspace uses three email standards to prevent mail. Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting Conformance (DMARC). The spoofing message is used for malicious processes. It is used to send harmful software and false information. This message is used in phishing to trick people into entering user information. Spammers forge messages to appear as well-known organizations. If they use your organization’s name to send messages users will report them as spam.

How to protect against email spoofing and phishing?
DMARC protects against email spoofing and phishing and prevents messages from being marked as spam. It is a standard email authentication method that helps administrators prevent hackers and attackers from spoofing their organization and domain. Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting Conformance also requests the email servers for the reports that have information to help you identify authentication issues and malicious activity for messages sent from your domain. DMARC tells the receiving servers what to do with outgoing messages from your organization that did not pass SPF or DKIM.

Things you must do before setting up DMARC
- Set up SPF and DKIM for your Domain.
- Set up a group or mailbox for DMARC reports.
- Get your domain host sign-in information.
- Check for an existing DMARC record (optional).
- Make sure third-party mail is authenticated.
How to define your DMARC Record
Your Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance policy in a line of text values is called a DMARC record. The DMARC record defines how strictly DMARC should check messages and Recommend actions for the receiving server when it gets messages that fail authentication checks.
The DMARC Record has three options
- Policy options
- Alignment Options
- Report options
DMARC policy options
Your DMARC policy recommends to the receiving mail server the action to take when a message from your domain does not pass DMARC authentication.
Example of a DMARC policy record: The v and p tags must be listed first and other tags can be in any order:
v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:[email protected], mail to:[email protected]; pct=100; adkim=s; aspf=s
When you start using DMARC, we recommend a policy with enforcement set to none. As you learn how messages from your domain are authenticated by receiving servers, update your policy. Over time, change the receiver policy to quarantine and finally to reject.
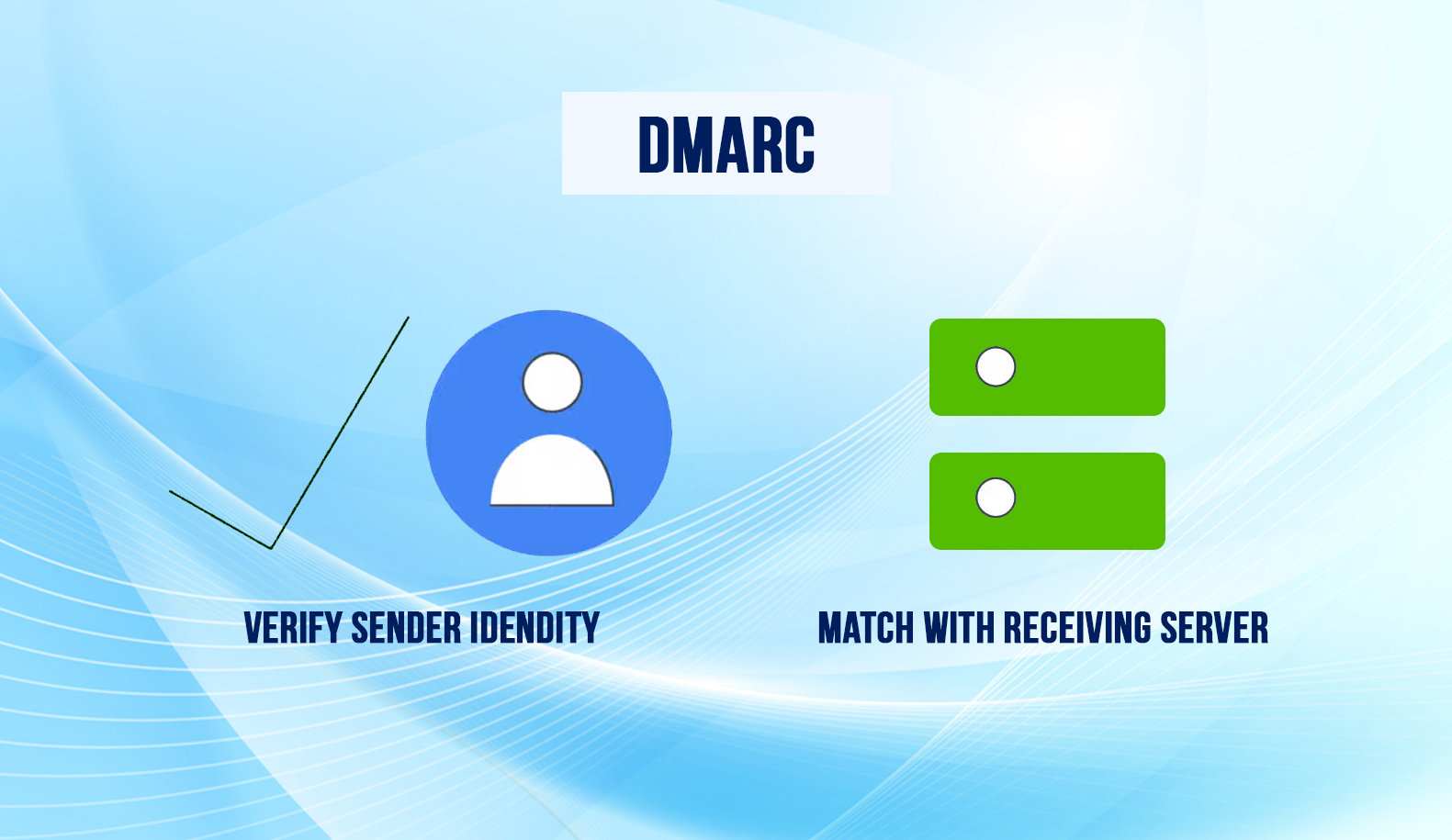
DMARC Alignment Options
DMARC passes or fails a message based on how closely the message from the header matches the sending domain specified by SPF or DKIM. It is called DMARC alignment.
You can choose from two alignment modes: strict and relaxed. Set the alignment mode for SPF and DKIM in the DMARC record. The SPF and DMARC record tags set the alignment mode.
We recommend you consider changing to strict alignment for increased protection against spoofing in the following cases,
- Mail sent for your domain from a subdomain outside your control
- You have subdomains managed by another entity
The message must pass at least one of these checks SPF authentication, SPF alignment, DKIM authentication, and DKIM alignment. If a message fails the DMARC check if the message fails SPF (or SPF alignment), DKIM (or DKIM alignment).
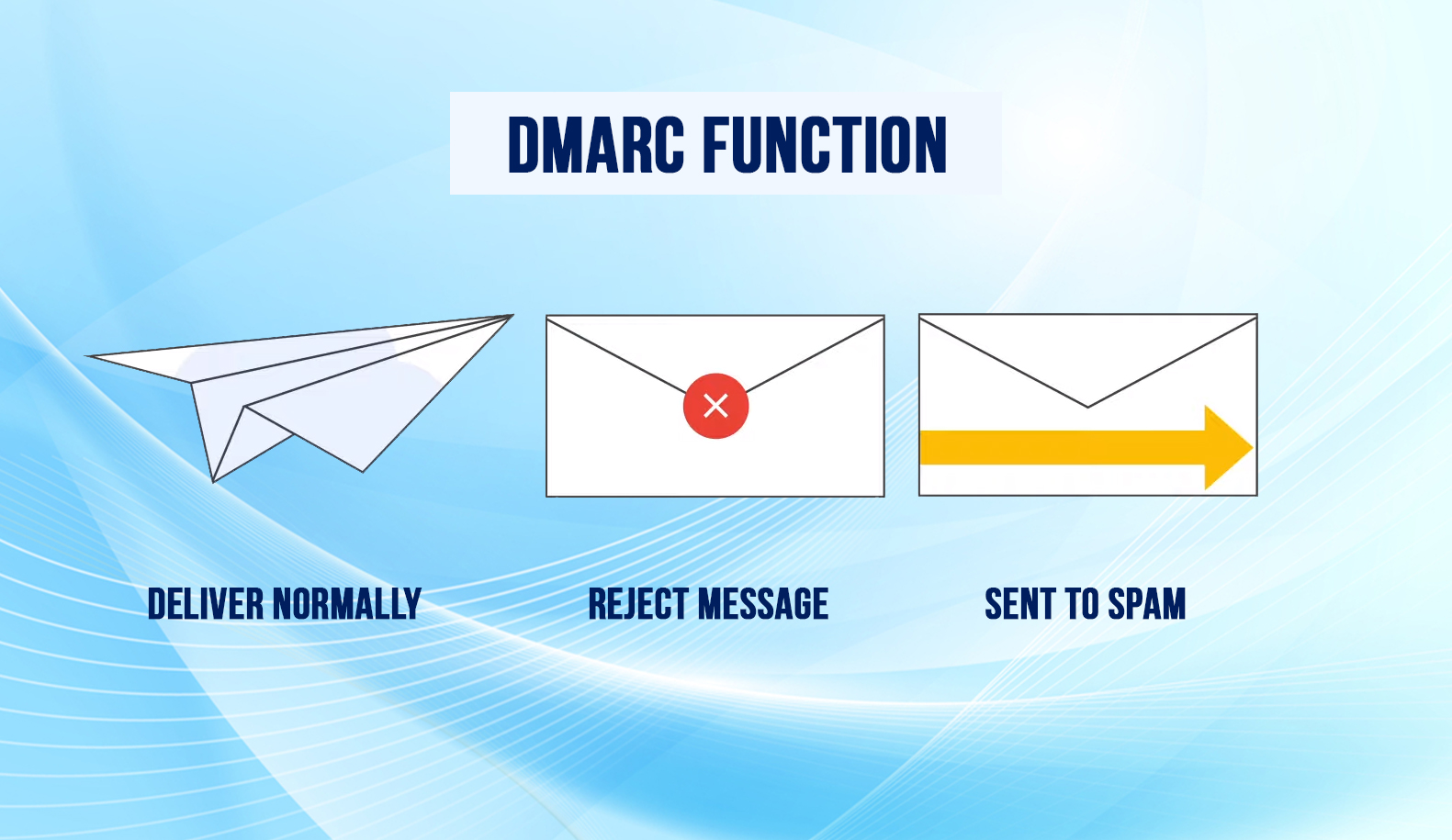
DMARC report options
You can set up DMARC to request regular reports from email servers that get email from your domain. DMARC reports tell about Servers or third-party senders sending mail to your Domain. Percent of messages from your domain pass DMARC. Servers or services are sending messages that fail DMARC. DMARC actions receiving server take on unauthenticated messages from your Domain. To start getting DMARC reports, use the rua DMARC record tag in your DMARC record.
How to add or update the DMARC Record
Do these steps in the management console for your domain host and not in the Admin console.
Have the text file or line that represents your policy record ready.
- Sign in to the management console for your domain host.
- Locate the page where you update DNS records.
- Add a DNS TXT record or modify an existing Record.
- Enter your Record in the TXT record for dmarc:
TXT record name: In the first field, under the DNS Hostname, enter: _dmarc.abc.com.
(Some domain hosts automatically add the domain name after _dmarc. After you add the TXT record, you can verify the DMARC TXT record name to make sure it is formatted correctly)- TXT record value: In the second field, enter the text for your DMARC record, for example, v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected]
(The field names might be different for your provider. DNS TXT record field names can vary slightly from provider to provider).
- TXT record value: In the second field, enter the text for your DMARC record, for example, v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected]
- Save your changes.
Hope you now about how to Setup / add / update DMARC Record.
Navohosting is one of the best google workspace offers services to our clients like
- Google Workspace
- Domain & hosting
- Website design
How to set up a secure multipurpose internet mail extension
How to enable POP / IMAP on Google Workspace?
How to Setup New Google Workspace Email Routing Settings?
If you need any support from us please contact us..